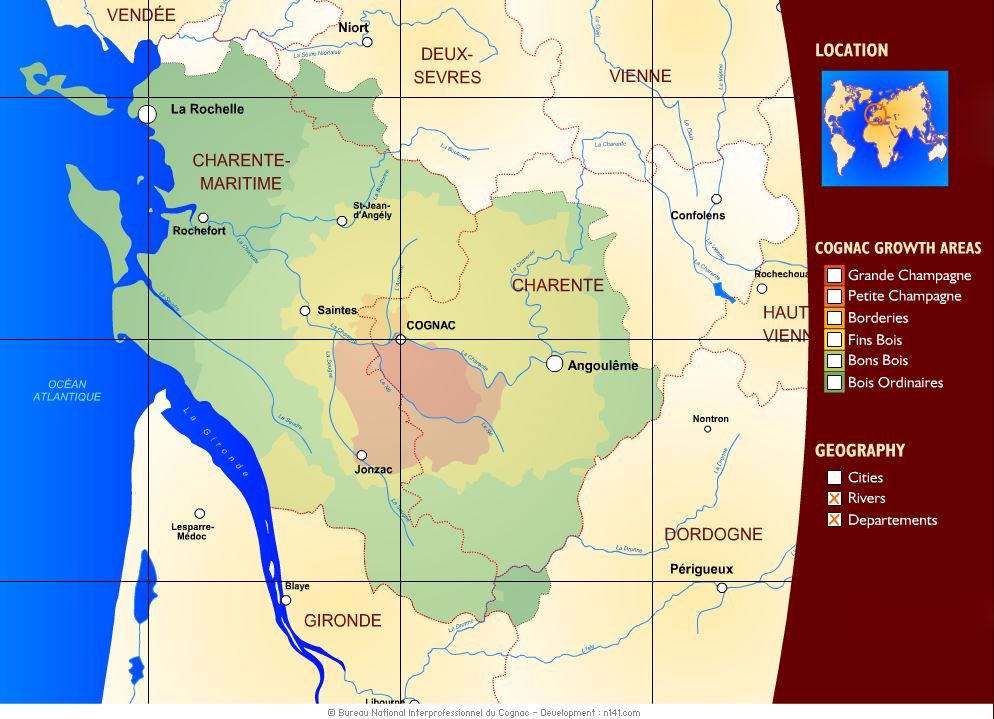
Here are the six crus (growing regions) in Cognac, listed in order of importance:
- Grande Champagne
- Petite Champagne
- Borderies
- Fins Bois
- Bons Bois
- Bois Ordinaires
Cognac is produced exclusively in the Cognac region of France, which is divided into six growing regions, known as “crus.” The six crus are Grande Champagne, Petite Champagne, Borderies, Fins Bois, Bons Bois, and Bois Ordinaires. Each cru has its own unique soil, climate, and topography, which can affect the flavor and character of the grapes grown there.
The two most prestigious crus are Grande Champagne and Petite Champagne, which are known for producing high-quality, elegant Cognacs with floral, fruity, and spicy notes. These regions have a chalky soil that retains moisture and regulates the vine’s growth, producing grapes with a high level of acidity and a low alcohol content.
Borderies is a smaller, more exclusive cru that is known for producing Cognacs with a distinctive nutty, spicy, and floral character. The soil in Borderies is clay-limestone, which produces grapes with a high alcohol content and a low acidity.
The Fins Bois, Bons Bois, and Bois Ordinaires crus are less prestigious than the other three, but they still produce good-quality Cognacs. Fins Bois is known for producing fruity, floral, and spicy Cognacs, while Bons Bois and Bois Ordinaires produce Cognacs with a more rustic, earthy character.
In summary, the six crus of the Cognac region are different in terms of soil, climate, and topography, which can affect the flavor and character of the grapes grown there. The most prestigious crus are Grande Champagne and Petite Champagne, which are known for producing high-quality, elegant Cognacs, while the other three crus produce Cognacs with a more rustic or distinctive character.